What are Flame Retardants?
Foam insulation is widely used in modern buildings to improve energy efficiency. Foam insulation helps to reduce energy consumption as well as making buildings and homes more energy efficient. This is important given that energy consumption in buildings is responsible for some 40% CO2 emissions.
Building insulation foams are flammable and their application and use in buildings is strictly controlled through regulations and flammability requirements. Such flammability requirements ensure that the insulation systems have sufficient flame retardancy to be used safely.
Brominated flame retardants added to insulation foams in precise quantities enhance the flame retardancy of the foams, helping to inhibit ignition or slow down the process of combustion.
A new generation of brominated flame retardants: Butadiene Styrene Co-polymer
As HBCD is being phased out globally, manufacturers of thermal insulation foams now have a more sustainable alternative flame retardant.
As an alternative to HBCD an innovative brominated polymeric flame retardant (FR) has been developed to provide effective flame retardant performance in polystyrene foams such as Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS).
These foams, commonly used in building and construction, ensure that homes, offices and public buildings are energy efficient and comfortable, whilst meeting fire safety requirements.
High molecular weight brominated polymer: the efficient, non-hazardous solution
This flame retardant exhibits a superior environmental profile to that of HBCD – being stable, with a high molecular weight. It is also classified as a nonhazardous polymer and as a Polymer of Low Concern(PLC) with officially recognised environment, health & safety characteristics.
Polymeric flame retardants, generally speaking, are inherently sustainable substances. Their high molecular weight makes them unlikely to penetrate through the cell membranes of living tissues. They are therefore not likely to be bioavailable and to bioaccumulate in the food chain.
In the last 20 years, there has been a dramatic rise in the amount and variety of electrical and electronic equipment in the home, workplace and in public spaces. In Europe for instance, the number of electronic appliances units traded grew by 13% between 2014 and 2017.
The proliferation of devices has been matched by a step change in their design (size, weight, materials) and production. TV screens are now as thin as plate glass with laptops and notepad devices even lighter.
Plastics are the dominant material used in the manufacture of electrical and electronic devices due to their versatility, diversity, mouldability and lightweight nature. Because of the high volume of plastics present, such equipment presents a fire risk. It is vital, to prevent fire and for human safety, that appliances and devices are resistant to ignition from the inside and can resist ignition from external sources.
Brominated flame-retardants provide the necessary flame retardancy to achieve both of these requirements. They can either be added to polymer materials during manufacture or can be reacted with materials such as epoxy used in the manufacture of printed circuit boards.
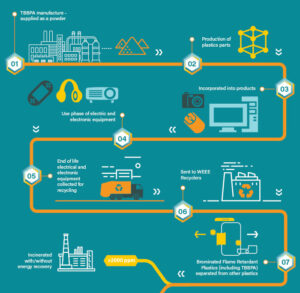
TBBPA in Electrical & Electronic Equipment
Chemical flame retardants are widely used to help meet specific standards for electrical and electronic equipment for particular components. Tetrabromobisphenol A – commonly known as TBBPA – serves a vital role in improving the fire safety of virtually all types of electronics as well as civilian and defence communication equipment. This is increasingly important given the miniaturisation of electronics, where more heat is produced within smaller devices.
TBBPA is the most widely used brominated flame retardant in the world. More than 90% of TBBPA produced is used in the production of FR4 type printed wired boards. In this application, TBBPA is used as a reactive flame retardant. In other words, it ceases to exist as a free chemical in the final board, becoming an integral part of the polymer matrix used to create the material for manufacturing the FR-4 printed circuit boards.
The remaining 10% of TBBPA produced is used in engineered plastics[3] in electrical and electronics products, meaning it is added to a polymer resin.
[3] Engineering plastics exhibit higher performance than standard materials, making them ideal for tough engineering applications. Engineering plastics have superior performance in the areas of heat resistance, chemical resistance, impact resistance, fire retardancy and mechanical strength. Plastics Europe
Modern homes contain a wide variety of materials used in different products and surface finishes. The vast majority of these are now synthetic materials – fibres and plastics. The versatility of these materials has enabled manufacturers to provide an increasingly diverse and practical range of products for homeowners.
While the extensive use of synthetic fibres brings advantages, the combination of some of these materials also creates challenges in terms of fire safety. Most developed economies have a range of fire safety regulations, codes and standards which seek to make furnishings and textiles safe from accidental fires caused by small ignition sources. These codes and standards do not mandate use of particular flame retardant technologies or indeed that any flame retardants are applied. Rather they require a flammability requirement to be met.
Brominated flame retardants are used either on their own or with a synergist (antimony trioxide) which reduced the overall amount of flame retardant needed.
Brominated flame-retardants ensure that the innovative materials used in trains, ships and road vehicles can be used safely and meet strict international fire safety standards.
Passenger aircraft represent a particular challenge for fire safety given the confined space. Aircraft carry a large amount of fuel and the cabin contains plastics, polymers and composites. As a result, stringent flame retardancy requirements are set in relevant aerospace standards established internationally. Brominated flame-retardants make an important contribution to enabling aircraft components and fittings meet these stringent fire safety requirements. Similarly, in trains and aircrafts where, seat covers and fillings, as well as vertical and horizontal panelling all need to be fire safe. Finally, materials used in cars are subject to a huge amount of daily thermal stress, which makes their use practically inconceivable without the application of flame-retardants including brominated flame-retardants.